Adjectives in English Grammar
What is an Adjective
What is an Adjective and What are its Types?
Adjectives English language को अधिक clear, meaningful और expressive बनाते हैं। ये किसी व्यक्ति, वस्तु या स्थान के गुण, संख्या, मात्रा, स्वामित्व या संकेत को स्पष्ट करते हैं।
Color, size, shape, feeling या quality—इन सभी को व्यक्त करने में adjective की महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका होती है।
Adjective (विशेषण):
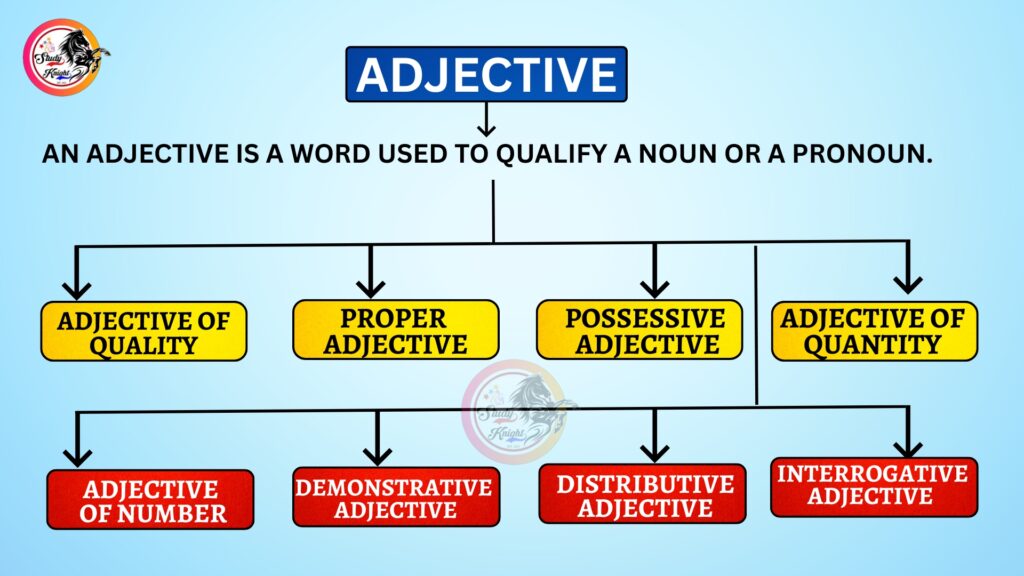
An adjective is a word that describes or modifies a noun or a pronoun.
(जो शब्द किसी संज्ञा (Noun) या सर्वनाम (Pronoun) की विशेषता बताए, उसे Adjective (विशेषण) कहते हैं।)
Examples:
- Ravi is a polite student.
- She is clever.
ऊपर दिए गए वाक्यों में polite और clever, क्रमशः Ravi और She की विशेषता बता रहे हैं, इसलिए ये Adjectives हैं।
👉 Adjective का प्रयोग सामान्यतः noun से पहले या linking verb के बाद होता है।Definition of AdjectiveAn adjective is a word that qualifies, describes, or limits the meaning of a noun or pronoun.Types of Adjective | Adjective के प्रकार
Adjectives को सामान्यतः आठ प्रकारों में बाँटा गया है—
- Adjective of Quality (गुणवाचक विशेषण)
- Proper Adjective (व्यक्तिवाचक विशेषण)
- Possessive Adjective (संबंधवाचक विशेषण)
- Adjective of Quantity (परिमाणवाचक विशेषण)
- Adjective of Number (संख्यावाचक विशेषण)
- Demonstrative Adjective (संकेतवाचक विशेषण)
- Distributive Adjective (विभागसूचक विशेषण)
- Interrogative Adjective (प्रश्नवाचक विशेषण)
Adjective of Quality (Descriptive Adjective)
Adjective of Quality वे adjectives होते हैं जो किसी व्यक्ति, वस्तु या स्थान के गुण या दोष को प्रकट करते हैं।
Modern English Grammar में इन्हें Descriptive Adjectives भी कहा जाता है।
Examples:
- Maharana Pratap was a brave warrior.
- The flower is fragrant.
इन वाक्यों में brave और fragrant क्रमशः Maharana Pratap और flower की विशेषता बता रहे हैं, इसलिए ये Adjectives of Quality हैं।
Descriptive Adjective की पहचान कैसे करें?
यदि किसी noun के साथ “कैसा / कैसी / कैसे” प्रश्न पूछा जाए और उत्तर मिले, तो वह शब्द Adjective of Quality होगा।
Example 1:
प्रश्न: महाराणा प्रताप कैसे योद्धा थे?
उत्तर: बहादुर (brave)
Example 2:
प्रश्न: फूल कैसा है?
उत्तर: सुगंधित (fragrant)
Proper Adjective (व्यक्तिवाचक विशेषण)
Proper Adjective:
Proper Adjectives वे adjectives होते हैं जो Proper Noun से बनाए जाते हैं और हमेशा Capital Letter से शुरू होते हैं। इनका प्रयोग किसी विशेष व्यक्ति, देश, स्थान या वस्तु की पहचान बताने के लिए किया जाता है।
👉 Examples (Proper Noun → Proper Adjective):
- India → Indian
- Italy → Italian
- Shakespeare → Shakespearean
Proper Adjectives को Adjective of Quality के अंतर्गत रखा जाता है क्योंकि ये भी किसी noun की विशेषता बताते हैं।
Examples:
- Indian culture is very rich.
- French perfume is famous worldwide.
- Japanese technology is advanced.
- British accent sounds elegant.
इन वाक्यों में Indian, French, Japanese, British Proper Nouns से बने हुए हैं, इसलिए ये Proper Adjectives हैं।
Possessive Adjective (संबंधवाचक विशेषण)
Possessive Adjective:
Possessive Adjectives वे adjectives होते हैं जो ownership या possession (अधिकार / संबंध) को दर्शाते हैं।
👉 Common Possessive Adjectives:
my, your, his, her, its, our, their
Examples:
- My bag is very heavy.
- Your answer is correct.
- His brother works abroad.
- Her painting won a prize.
- Our classroom is clean.
- Their house is near the park.
उपर्युक्त वाक्यों में my, your, his, her, our, their अपने-अपने nouns (bag, answer, brother, painting, classroom, house) से संबंध बता रहे हैं, इसलिए ये Possessive Adjectives हैं।
📌 Note:
Possessive Adjective हमेशा noun के साथ प्रयोग होता है।
Adjective of Quantity (परिमाणवाचक विशेषण)
Adjective of Quantity:
वे adjectives जो किसी noun की मात्रा (Quantity) को दर्शाते हैं, उन्हें Adjective of Quantity कहते हैं।
👉 Common words:
some, much, little, enough, all, any, no
Examples:
- She drank little water.
- We have enough time.
- He spent all his savings.
- I do not have any patience.
इन वाक्यों में little, enough, all, any मात्रा बता रहे हैं, इसलिए ये Adjectives of Quantity हैं।
पहचान (Identification Rule):
यदि noun के साथ “कितना” (How much) प्रश्न पूछा जाए और उत्तर मिले, तो वह Adjective of Quantity होगा।
Example:
प्रश्न: उसने कितना पानी पिया?
उत्तर: थोड़ा (little)
📘 “Adjectives of Quantity answer the question: How much?” — P. C. Wren
Adjective of Number / Numeral Adjective:
वे adjectives जो किसी व्यक्ति या वस्तु की संख्या या क्रम को बताते हैं, उन्हें Adjective of Number कहते हैं।
Examples:
- Seven students were absent.
- I bought three notebooks.
- She stood first in the race.
- He lives on the second floor.
इन वाक्यों में seven, three, first, second संख्या या क्रम बता रहे हैं, इसलिए ये Adjectives of Number हैं।
Types of Adjective of Number
- Cardinal Numbers (गणनावाचक)
👉 one, two, three, four, five आदि
- Five players were selected.
- Ordinal Numbers (क्रमवाचक)
👉 first, second, third, fourth आदि
- This is my first attempt.
📘 “Adjectives of Number answer the question: How many?”
Demonstrative Adjective (संकेतवाचक विशेषण)
Demonstrative Adjective:
Demonstrative Adjectives: वे adjectives होते हैं जो किसी विशेष Noun की ओर संकेत (point out) करते हैं। ये बताते हैं कि कौन-सी वस्तु या व्यक्ति की बात हो रही है।
👉 Common Demonstrative Adjectives:
this, that, these, those
संकेतवाचक विशेषण वह विशेषण होता है जो किसी संज्ञा की ओर इशारा करता है।
Examples of Demonstrative Adjective:
- This chair is comfortable. — यह कुर्सी आरामदायक है।
- That building is very old. — वह इमारत बहुत पुरानी है।
- These questions are important. — ये प्रश्न महत्वपूर्ण हैं।
- Those stars look beautiful. — वे तारे सुंदर लगते हैं।
इन वाक्यों में this, that, these, those क्रमशः chair, building, questions, stars की ओर संकेत कर रहे हैं, इसलिए ये Demonstrative Adjectives हैं।
Interrogative Adjective (प्रश्नवाचक विशेषण)
Interrogative Adjective:
Interrogative Adjectives का प्रयोग प्रश्न पूछने के लिए किया जाता है और ये हमेशा किसी noun के साथ आते हैं।
👉 Common Interrogative Adjectives:
which, what, whose
प्रश्नवाचक विशेषण वह विशेषण है जिससे किसी संज्ञा के बारे में प्रश्न किया जाता है।
Examples of Interrogative Adjective:
- Which subject do you like most? — तुम्हें कौन-सा विषय सबसे अधिक पसंद है?
- What movie are you watching? — तुम कौन-सी फिल्म देख रहे हो?
- Whose mobile is on the table? — मेज़ पर रखा मोबाइल किसका है?
- Which road leads to the station? — स्टेशन की ओर कौन-सी सड़क जाती है?
इन उदाहरणों में which, what, whose nouns के साथ प्रयोग होकर प्रश्न बना रहे हैं, इसलिए ये Interrogative Adjectives हैं।
Distributive Adjective (विभागसूचक विशेषण)
Distributive Adjective:
Distributive Adjectives किसी समूह के प्रत्येक सदस्य को अलग-अलग दर्शाते हैं, न कि पूरे समूह को एक साथ।
👉 Common Distributive Adjectives:
each, every, either, neither
विभागसूचक विशेषण वह विशेषण है जो किसी वर्ग या समूह की प्रत्येक वस्तु या व्यक्ति को अलग-अलग प्रकट करता है।
Examples of Distributive Adjective:
- Each student must wear an ID card. — प्रत्येक विद्यार्थी को पहचान पत्र पहनना चाहिए।
- Every employee received a bonus. — प्रत्येक कर्मचारी को बोनस मिला।
- Either answer is correct. — दोनों में से कोई भी उत्तर सही है।
- Neither road is safe at night. — दोनों में से कोई भी सड़क रात में सुरक्षित नहीं है।
इन वाक्यों में each, every, either, neither का प्रयोग Distributive Adjective के रूप में हुआ है।
Important Notes (ध्यान रखें):
- Each, Every, Either, Neither के बाद Noun का प्रयोग अनिवार्य है।
- Either का अर्थ — दोनों में से कोई एक (Positive)
- Neither का अर्थ — दोनों में से कोई नहीं (Negative)
Use of Descriptive Adjective (गुणवाचक विशेषण का प्रयोग)Descriptive Adjective को Adjective of Quality भी कहा जाता है। इसका प्रयोग दो तरीकों से किया जाता है:
- Attributive Use
जब Adjective, Noun से पहले आए।
- Predicative Use
जब Adjective, Verb के बाद आए।
Attributive Use | Predicative Use |
A brave soldier fought. | The soldier is brave. |
A clean room looks nice. | The room is clean. |
A clever girl won. | The girl is clever. |
An honest officer resigned. | The officer is honest. |
पहले कॉलम में Adjectives, Noun से पहले हैं — यह Attributive use है।
दूसरे कॉलम में Adjectives, Verb के बाद हैं — यह Predicative use है।
Test Yourself (Practice Questions)
नीचे दिए गए वाक्यों में से Adjectives पहचानिए और बताइए कि वे किस प्रकार के हैं:
- The elephant is a strong animal.
- Rohit is a smart and active boy.
- This pen writes smoothly.
- She bought some fruits.
- Those buildings are tall.
- I have no money today.
- Each player received a medal.
- Which dress will you wear?
- The sky looks dark and cloudy.
- Give me that file.
Additional Categories of Adjectives
Quantitative Adjectives
These adjectives show the amount or quantity of a noun. Common examples are one, two, few, many, some, several, all, etc.
Examples:
- three kittens
- many novels
- a few classmates
- all employees
Comparative Adjectives
These adjectives are used to compare two people, places, or things. Words like better, worse, taller, smaller, more, and less are commonly used.
Examples:
- She is taller than her sister.
- This movie is more engaging than the previous one.
Superlative Adjectives
Superlative adjectives compare more than two things and show the highest degree of a quality. They include best, worst, tallest, smallest, most, and least.
Examples:
- He is the tallest player on the team.
- This is the most delicious dish here.
Indefinite Adjectives
These adjectives give a vague or general idea about the noun without being specific. Examples include some, any, several, many, few, and all.
Examples:
- Some students prefer online classes.
- Many options are available.
Compound Adjectives
Compound adjectives are made by joining two or more words, often with a hyphen, to describe a noun.
Examples:
- well-prepared
- high-speed
- blue-green
- ten-year-old
Predicate Adjectives
These adjectives come after linking verbs such as is, are, was, become, seem, or appear and describe the subject.
Example:
- The child is curious.
Participial Adjectives
Formed from verbs, these adjectives usually end in -ed or -ing and describe a noun or pronoun.
Examples:
- a broken window
- an exciting match
Ordinal Adjectives
Ordinal adjectives show the order or position of nouns in a sequence.
Examples:
- the first prize
- the second lesson
- the final chapter
Emphasizing Adjectives
These adjectives are used to strongly stress or intensify a noun’s quality.
Examples:
- a total success
- sheer brilliance
- complete silence
Interjectional Adjectives
Such adjectives express strong feelings or reactions and are often found in exclamatory sentences.
Examples:
- amazing performance
- incredible achievement
Color Adjectives
They describe the color of a noun.
Examples:
- a golden ring
- a white shirt
- a black car
Time Adjectives
These adjectives relate to time or frequency.
Examples:
- an early train
- a daily routine
- an annual report
Spatial Adjectives
Spatial adjectives describe position, direction, or location.
Examples:
- the front door
- the upper shelf
- the inner room
Material Adjectives
These adjectives show what material an object is made of.
Examples:
- a marble statue
- a leather jacket
- a glass bowl
Nationality Adjectives
Nationality adjectives indicate the origin or nationality of a noun.
Examples:
- an Italian artist
- a Japanese company
- an Indian festival
Size Adjectives
Size adjectives are used to show the size or dimensions of a noun. Words like big, small, tiny, huge, massive, enormous come under this category.
Examples:
- a huge building
- a small kitten
- a tiny button
Sound Adjectives
Sound adjectives describe how something sounds or the nature of a sound. Common examples are loud, soft, noisy, silent, pleasant, harsh, etc.
Examples:
- a noisy street
- a soft voice
- a pleasant tune
Taste and Smell Adjectives
These adjectives tell us about taste or smell. Words such as sweet, sour, bitter, spicy, fragrant, aromatic are used here.
Examples:
- a spicy dish
- a sour lemon
- an aromatic perfume
ध्यान रखें कि कई बार एक adjective एक से अधिक categories में भी आ सकता है। ये extra types noun या pronoun को और ज्यादा clear और specific बनाते हैं।
Degrees (Forms) of Adjectives
Degrees of adjectives noun की quality या intensity को compare करने के different levels दिखाते हैं। Adjectives की three degrees of comparison होती हैं।
विशेषणों (Adjectives) की तुलनात्मक अवस्थाएँ तीन होती हैं—
- Positive Degree (मूल अवस्था)
- Comparative Degree (उच्चतर अवस्था)
- Superlative Degree (उच्चतम अवस्था)
Positive Degree
Positive degree adjective का simple form होता है, जिसमें कोई comparison नहीं होता।
जब adjective का प्रयोग सामान्य रूप में किया जाता है, तब Positive Degree का use होता है।
Examples:
- The puppy is cute.
- Rohit is a smart boy.
- This place is calm.
Comparative Degree
Comparative degree दो व्यक्तियों, वस्तुओं या स्थानों के बीच तुलना के लिए use होती है।
Short adjectives में -er और long adjectives के साथ more का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
जब किसी के गुण या दोष की तुलना किसी दूसरे से की जाती है, तब Comparative Degree का प्रयोग होता है।
Examples:
- The puppy is cuter than the cat.
- This road is longer than that one.
- Rohit is smarter than Aman.
- Which of these two cars is faster?
Superlative Degree
Superlative degree का प्रयोग तब किया जाता है जब comparison पूरे group के साथ किया जाए।
Short adjectives में -est और long adjectives के साथ most का प्रयोग होता है।
जब किसी एक व्यक्ति, वस्तु या स्थान को पूरे group में सबसे ऊपर या नीचे दिखाया जाए, तब Superlative Degree use होती है।
Examples:
- The puppy is the cutest in the park.
- This is the most interesting story.
- Rohit is the smartest student in the class.
- Mount Everest is the highest peak in the world.
Formation of Comparative and Superlative Degrees
The comparative and superlative degrees of adjectives are formed using different patterns, depending on the length and structure of the adjective.
Rules for Forming Comparative and Superlative Degrees
Rule 1: One-syllable adjectives
For most one-syllable adjectives, add -er to form the comparative degree and -est to form the superlative degree.
Positive | Comparative | Superlative |
tall | taller | tallest |
fast | faster | fastest |
strong | stronger | strongest |
cold | colder | coldest |
deep | deeper | deepest |
high | higher | highest |
kind | kinder | kindest |
poor | poorer | poorest |
small | smaller | smallest |
Rule 2: One-syllable adjectives ending in -eIf the adjective ends in -e, add -r for the comparative and -st for the superlative.
Positive | Comparative | Superlative |
large | larger | largest |
fine | finer | finest |
brave | braver | bravest |
close | closer | closest |
safe | safer | safest |
Rule 3: One-syllable adjectives ending in -y (with a consonant before it)Change y to i and then add -er or -est.
Positive | Comparative | Superlative |
easy | easier | easiest |
heavy | heavier | heaviest |
happy | happier | happiest |
busy | busier | busiest |
pretty | prettier | prettiest |
funny | funnier | funniest |
tidy | tidier | tidiest |
Rule 4: One-syllable adjectives ending in a single consonant with a vowel before itDouble the final consonant before adding -er or -est.
Positive | Comparative | Superlative |
big | bigger | biggest |
fat | fatter | fattest |
hot | hotter | hottest |
red | redder | reddest |
sad | sadder | saddest |
wet | wetter | wettest |
Rule 5: Adjectives with two or more syllables
Use more before the adjective for the comparative degree and most for the superlative degree.
Positive | Comparative | Superlative |
beautiful | more beautiful | most beautiful |
intelligent | more intelligent | most intelligent |
creative | more creative | most creative |
delicious | more delicious | most delicious |
peaceful | more peaceful | most peaceful |
interesting | more interesting | most interesting |
important | more important | most important |
comfortable | more comfortable | most comfortable |
powerful | more powerful | most powerful |
Rule 6: Irregular adjectives Some adjectives do not follow standard rules. Their forms must be memorized.
Positive | Comparative | Superlative |
good | better | best |
well | better | best |
bad | worse | worst |
little | less | least |
much | more | most |
many | more | most |
old | older | oldest |
old | elder | eldest |
late | later | latest |
Important Usage Notes
- Much is used with uncountable nouns (quantity).
Example: I have much work to do. - Many is used with countable nouns (number).
Example: She has many friends. - Older / Oldest are used for both people and things.
Example: This is the oldest building in the city. - Elder / Eldest are used only for family members and are not followed by than.
Example: He is my elder brother. - Adjectives like junior, senior, superior, inferior are followed by to, not than.
Examples:- I am junior to him.
- This product is superior to that one.
• Most asked Question from Adjective
- What is an adjective?
- An adjective is a word that describes or modifies a noun or pronoun by providing additional information about its qualities, characteristics, or attributes.
- What is the function of an adjective in a sentence?
- The function of an adjective is to add descriptive or qualitative information to a noun or pronoun, helping to provide a clearer or more detailed picture of the subject.
- What are the different types of adjectives?
- Adjectives can be categorized into various types, including descriptive adjectives, quantitative adjectives, demonstrative adjectives, possessive adjectives, interrogative adjectives, and more.
- How are comparative and superlative degrees formed?
- Comparative degrees of adjectives are formed by adding “-er” at the end or by using “more” before the adjective. Superlative degrees are formed by adding “-est” at the end or by using “most” before the adjective. However, irregular adjectives have unique comparative and superlative forms.
- What is the role of adjectives in sentence structure?
- Adjectives primarily serve to modify nouns or pronouns, but they can also be used attributively (before the noun) or predicatively (after linking verbs) in a sentence.
- Can adjectives be used to compare more than two items?
- Yes, adjectives can be used to compare more than two items through the use of phrases like “more than,” “less than,” or “as…as.”
- Can adjectives be used in a sentence without a noun?
- Yes, adjectives can function as standalone predicates or be used in comparative or superlative forms without directly modifying a noun.
- Can adjectives have degrees of comparison in all situations?
- While most adjectives can have comparative and superlative forms, some adjectives, such as “unique” or “perfect,” do not typically have degrees of comparison.
- Can adjectives be used to compare non-tangible or abstract concepts?
- Yes, adjectives can be used to compare non-tangible or abstract concepts by using figurative language or metaphorical comparisons.
- How can I improve my use of adjectives in writing or speech?
- To improve your use of adjectives, expand your vocabulary, read extensively, practice describing things in detail, and experiment with different adjectives to convey specific meanings and create vivid imagery.